Intro
Wappler now makes it easy to configure HTTP Security Headers in your Node.js projects through the built-in Helmet middleware.
These headers help protect your app from common web vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking, and content injection attacks, all without manual server configuration.
[!note]
The HTTP Security Headers (Helmet) middleware is available only for Node.js projects.
What Are HTTP Security Headers?
HTTP Security Headers are special instructions your server sends along with every response to a browser.
They tell the browser how to handle your website’s content securely — for example, which resources it can load, whether it’s allowed to be embedded in an iframe, or if it should always use HTTPS.
These headers act as a first line of defense between your application and potential attacks.
Even if your code is secure, missing or misconfigured headers can expose your users to vulnerabilities such as:
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) – Malicious scripts injected into your pages.
- Clickjacking – Attackers embedding your site inside an invisible frame to trick users into clicking.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks – When HTTP is used instead of HTTPS.
- Data Leakage – Sending referrer or resource data to untrusted domains.
Modern browsers understand these headers and strictly enforce the rules they define — making them one of the most effective and lightweight ways to improve your app’s security and privacy.
Wappler integrates the popular Helmet middleware to simplify this process.
With a few clicks, you can configure all key HTTP security headers visually in Server Connect Settings, ensuring your Node.js server automatically applies the correct headers for every request.
Configuring HTTP Security Headers
Wappler lets you configure security headers either globally for your Node.js project using Helmet, or per page using Meta Tags.
Both approaches help enforce browser-level security and protect your app from cross-site scripting, clickjacking, and similar attacks.
Server Connect Settings (Helmet Middleware)
For Node.js projects, the recommended way to manage security headers is through the Helmet settings.
These settings apply globally to all API routes and pages served by your server.
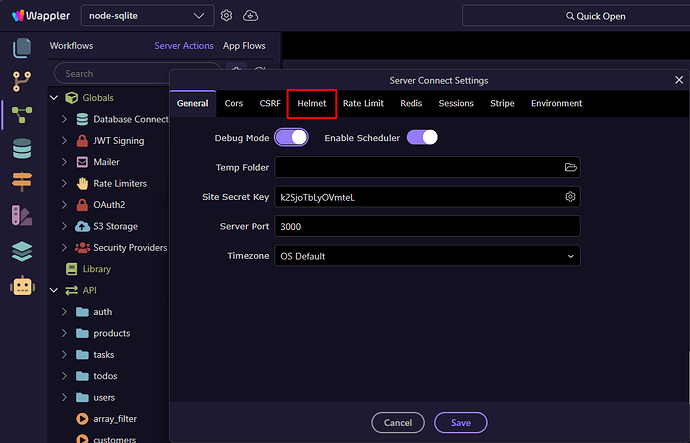
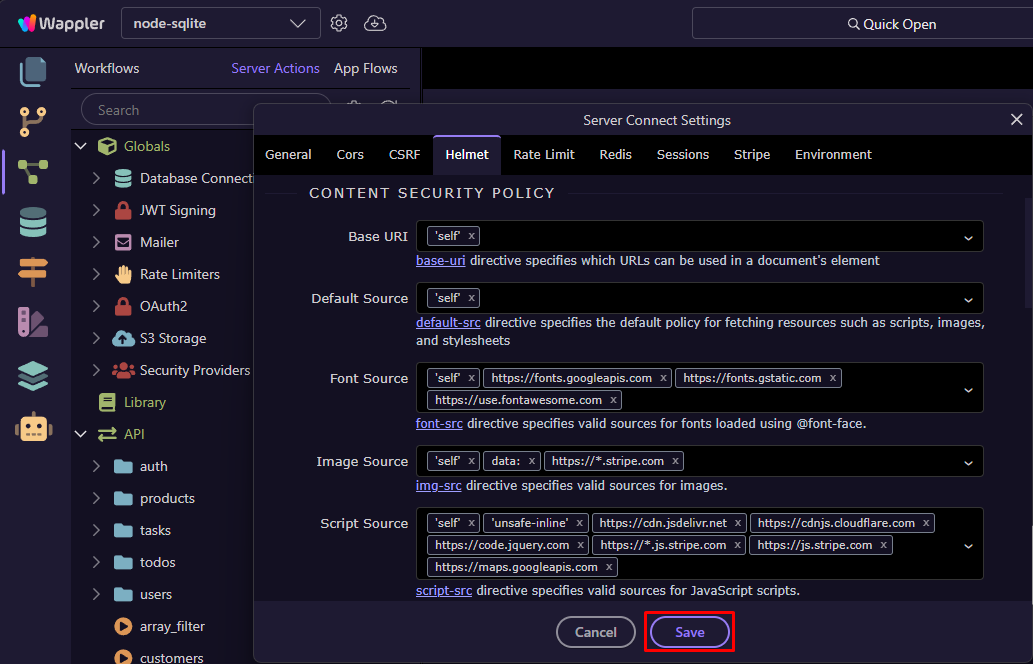
To configure, open Server Connect Settings → Helmet:
Enable the Helmet toggle:
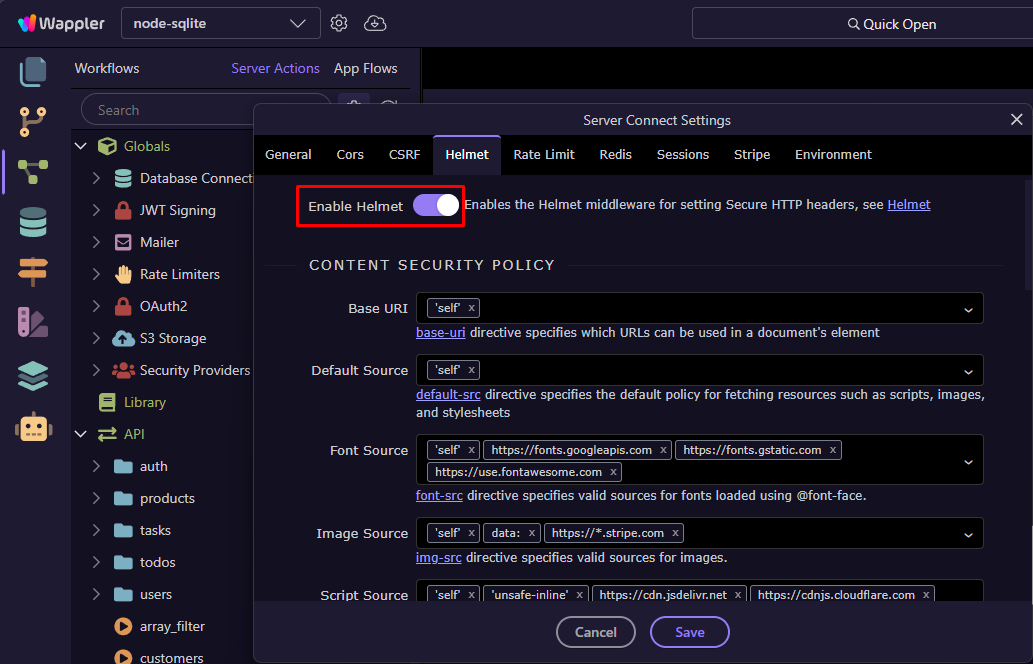
Adjust your Content Security Policy (CSP) and other header options as needed:
Click Save — the headers will be automatically added to every server response:
[!tip]
The default Helmet settings in Wappler already include secure and well-balanced defaults that cover most use cases.
They are designed to ensure proper protection while maintaining full compatibility with Wappler’s built-in components and common external resources.
You only need to modify them if your app loads content from additional domains, custom APIs, or third-party scripts.
Below is a list of all headers you can configure using Helmet in Wappler, along with links to their MDN documentation.
Content Security Policy (CSP)
Defines which external resources your app is allowed to load, helping to prevent XSS and injection attacks.
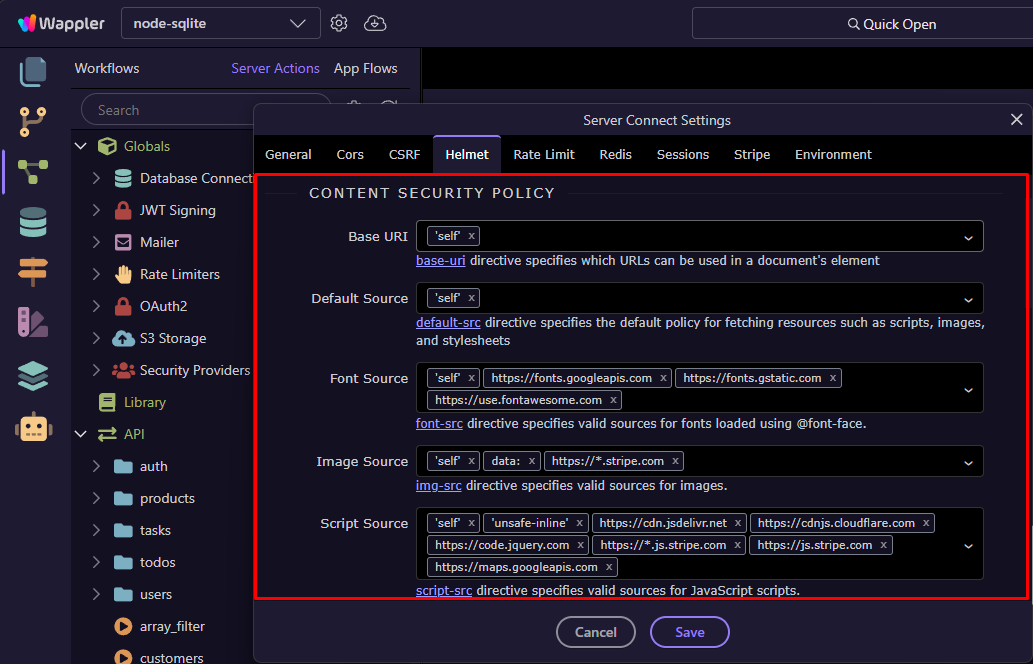
- base-uri — Restricts URLs that can appear in the
<base>element. - default-src — Fallback policy for all unspecified resource types.
- font-src — Allowed sources for web fonts.
- img-src — Allowed sources for images.
- script-src — Allowed sources for JavaScript files and inline scripts.
- style-src — Allowed sources for CSS stylesheets.
- frame-src — Allowed sources for iframes.
- connect-src — Allowed endpoints for fetch, XHR, and WebSocket connections.
Cross-Origin Policies
- Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy — Isolates your browsing context from other origins for better security.
- Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy — Prevents other sites from embedding or fetching your resources.
Referrer Policy
- Referrer-Policy — Controls how much referrer information is sent when navigating away from your site.
Transport Security
- Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS) — Forces browsers to always use HTTPS connections.
Content Type and Framing
- X-Content-Type-Options — Prevents browsers from MIME-type sniffing.
- X-DNS-Prefetch-Control — Controls whether the browser prefetches DNS requests.
- X-Frame-Options — Prevents clickjacking by disallowing your site from being embedded in frames.
[!info]
Learn more about Helmet at helmetjs.github.io.
Customizing Properties
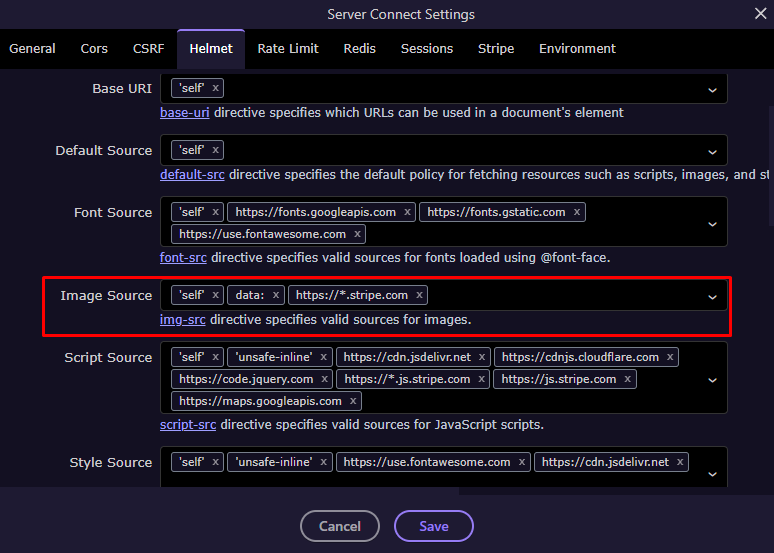
If your project needs to load resources from additional trusted domains — for example, images from Unsplash —
you can easily extend the default security settings in the Helmet configuration.
Scroll down to the Content Security Policy (CSP) section and find the directive you want to modify — in this case, Image Source (img-src):
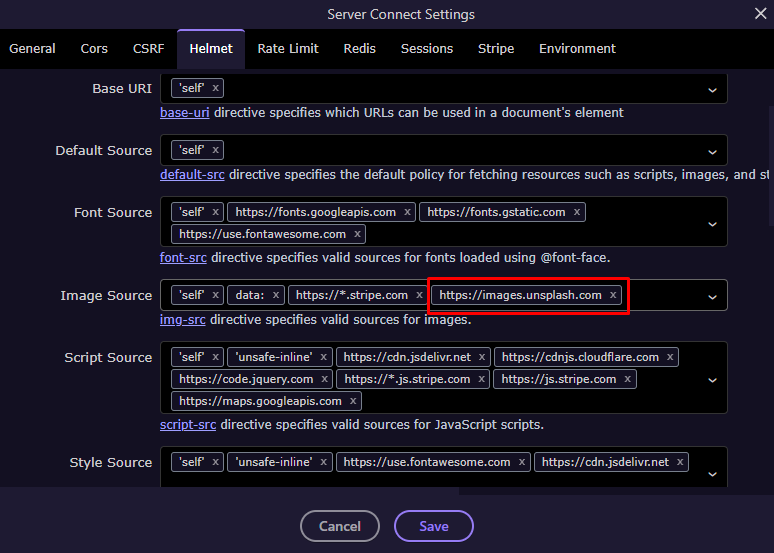
Click inside the input field and add the new domain to the list. For Unsplash enter https://images.unsplash.com and then hit the Enter key:
Click Save and you are done.
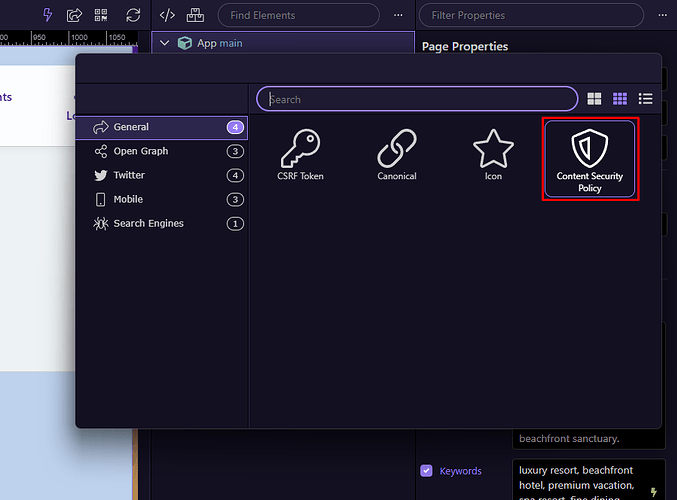
Page Meta Tags (Page-Level CSP)
If your project doesn’t use a Node.js backend — such as a frontend-only site, static page, or mobile app built with Framework7 or Capacitor —
or if you simply want to apply page-specific Content Security Policies within a Node.js project,
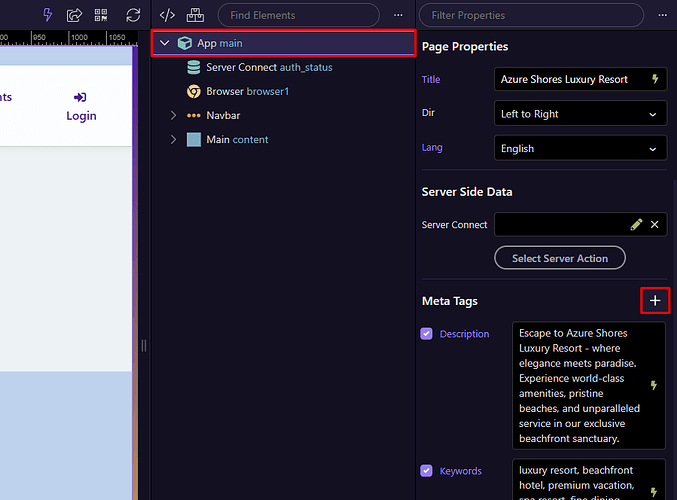
you can define them directly using Meta Tags in the App Structure panel.
To configure, in App Structure select App → Meta Tags → Content Security Policy in the App Structure panel. For Node.js, this should be applied on the Layout (main) pages:
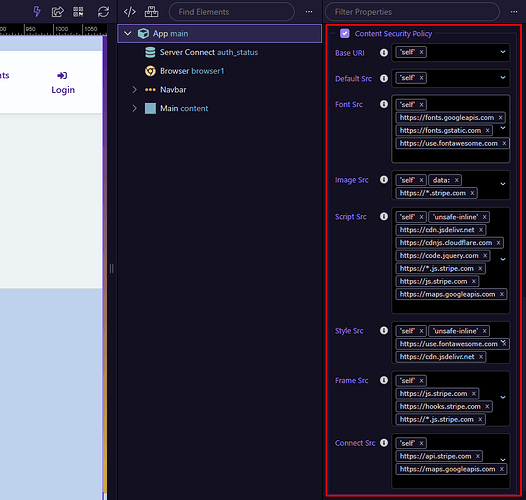
Define allowed sources for scripts, images, styles, fonts, or connections:
Wappler will automatically inject the correct <meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy"> tag into the page’s <head>.
[!note]
Meta-based CSP only applies to the current page.
It cannot enforce certain headers likeStrict-Transport-SecurityorX-Frame-Options.
Below is a list of all available CSP Directives you can configure along with links to their MDN documentation.
- base-uri — Restricts URLs that can appear in the
<base>element. - default-src — Fallback policy for all unspecified resource types.
- font-src — Allowed sources for web fonts.
- img-src — Allowed sources for images.
- script-src — Allowed sources for JavaScript files and inline scripts.
- style-src — Allowed sources for CSS stylesheets.
- frame-src — Allowed sources for iframes.
- connect-src — Allowed endpoints for fetch, XHR, and WebSocket connections.
[!tip]
For an overview of supported CSP directives, see MDN Web Docs – Content Security Policy Overview.
Summary
With Wappler’s built-in Helmet middleware and Meta Tag configuration, you can easily manage all essential HTTP Security Headers without writing custom code.
Whether you choose global server-level protection or page-specific policies, these settings provide a strong, flexible foundation for securing your web apps against common vulnerabilities.